+86 180 0293 5268
+86 180 0293 5268
Can Titanium Bolt Fully Replace Stainless Steel Bolt?
Although titanium bolt offer advantages such as high strength, lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and non-magnetic characteristics, whether they can fully replace stainless steel bolt requires a comprehensive discussion based on cost factors, performance characteristics, application scenarios, and manufacturing processes:
-
l Material Costs
Titanium is a relatively scarce global resource with complex extraction and refining processes, resulting in significantly higher material costs. In contrast, stainless steel (composed primarily of iron, chromium, and nickel) benefits from abundant raw material reserves and lower production costs.l Manufacturing Costs
Titanium alloy machining is highly challenging, requiring specialized equipment (e.g., high-temperature vacuum or inert gas environments for smelting) and precision CNC machining, tool wear is severe, and machining efficiency is low. stainless steel, with its mature and optimized manufacturing processes, offers far lower machining costs and higher production efficiency.
2. Performance Characteristics
l Strength
While titanium bolts exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios, high-strength stainless steel bolts may be more practical in applications requiring extreme static load resistance (e.g., large-scale construction, bridges). Stainless steel’s higher yield and tensile strength ensure reliable performance under heavy loads.
l Corrosion resistance
Titanium performs exceptionally well in most corrosive environments. However, in high-temperature, high-concentration chemical media (e.g., hydrochloric or sulfuric acid), certain stainless steel alloys (e.g., super duplex grades) demonstrate superior corrosion resistance, making them preferable for specialized industrial equipment like chemical reactors.
l Fatigue Resistance
Decades of research have refined stainless steel’s fatigue resistance. In applications with cyclic loading (e.g., machinery, automotive), high-grade stainless steel bolts often outperform titanium due to optimized metallurgical properties.
3. Application Scenarios
l Versatility
Stainless steel bolts dominate industries like construction, automotive, and appliances due to their cost-effectiveness and standardized specifications. Titanium bolts are niche solutions, primarily used in aerospace, medical implants, and other high-performance fields where weight savings and extreme durability justify the cost.
l Magnetic Properties
Titanium’s non-magnetic nature is critical for MRI machines and electronics. Conversely, stainless steel’s magnetic properties are advantageous in motors, transformers, and other electromagnetic applications.
4. Manufacturing Processes
l Cold Heading
Stainless steel bolts are efficiently mass-produced via cold heading. Titanium’s poor plasticity, high springback, and cracking risk necessitate preheated dies, multi-stage incremental forming, and specialized lubricants—significantly increasing complexity and cost.
l Machinability
Both materials can be machined, but titanium’s low thermal conductivity and work-hardening tendencies reduce tool life and productivity compared to stainless steel.
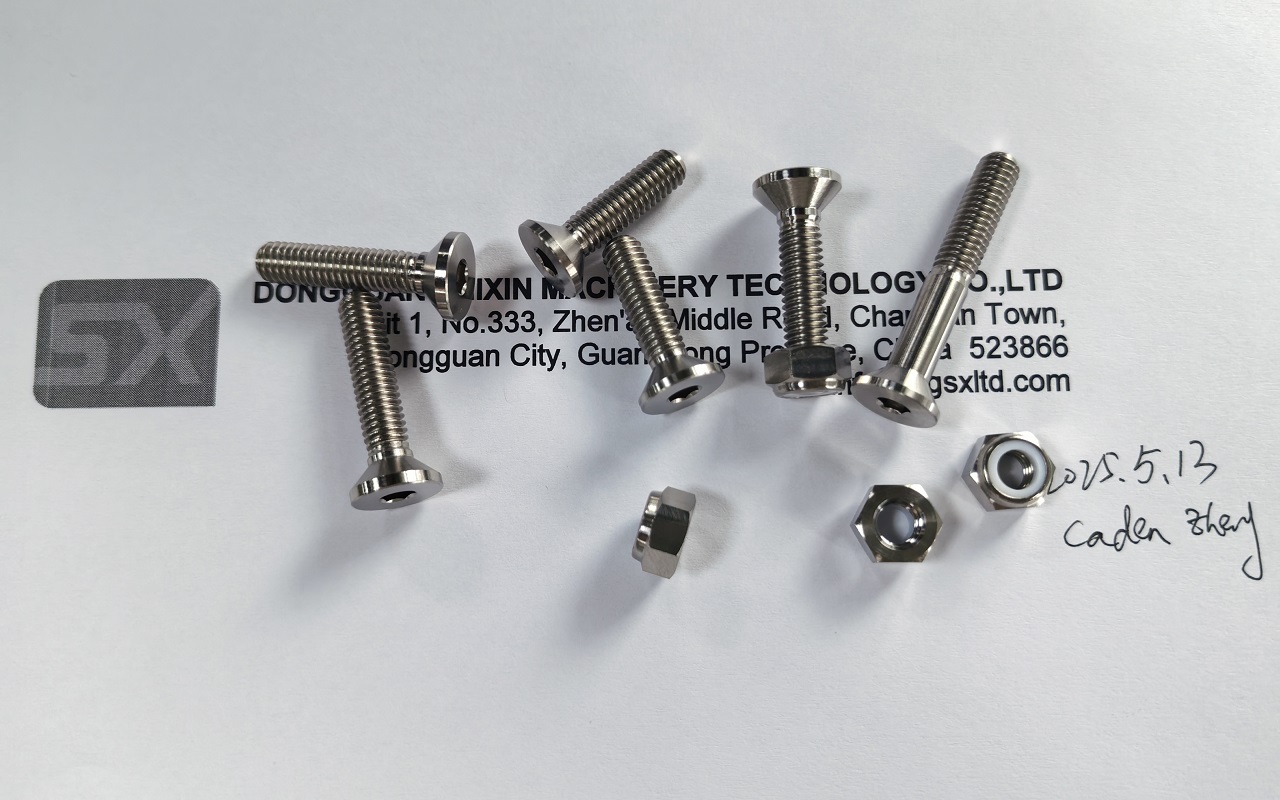

While titanium bolts excel in specialized applications, their high cost and processing constraints prevent broad replacement of stainless steel. Fundamental differences in material behavior and economics ensure stainless steel remains the dominant choice for cost-driven industries. However, advancements in titanium machining may expand its adoption in the future. Dongguan SX Technology Co.,Ltd. specializes in precision titanium machining. For technical collaboration or inquiries, contact us at info@dgsxltd.com