+86 180 0293 5268
+86 180 0293 5268
How to Reduce Porosity in Metal Casting?
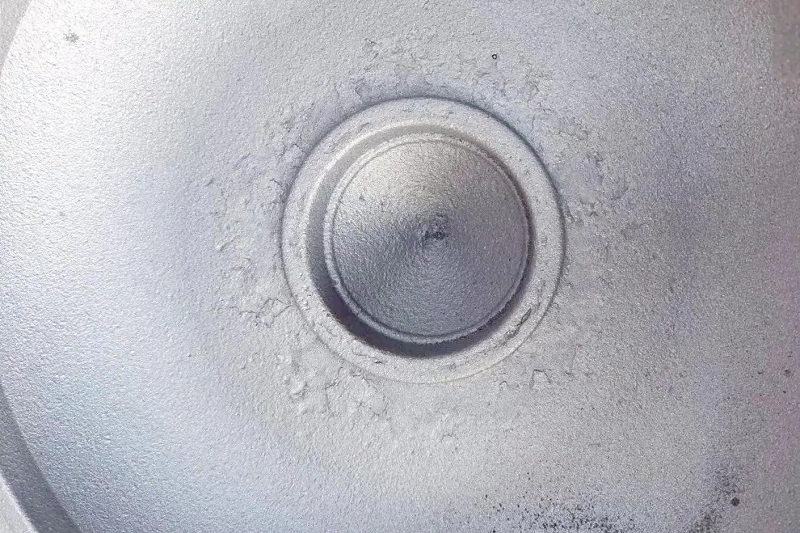
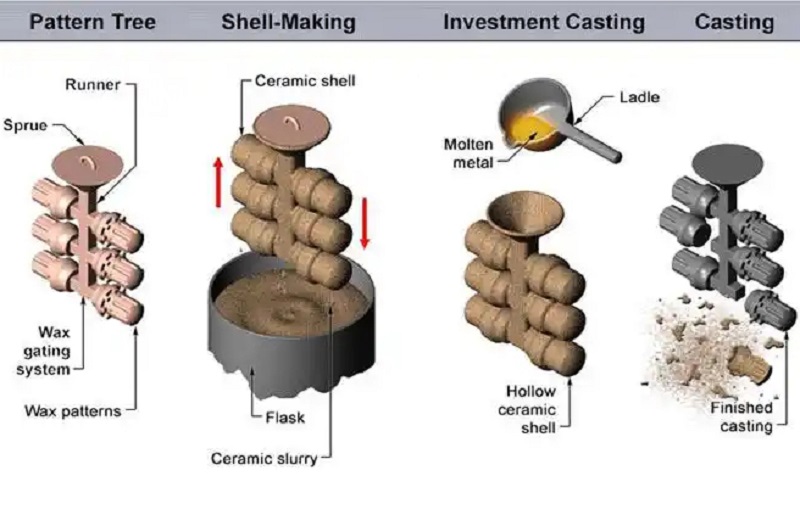
Gas porosity is one of the common defects in precision casting , manifesting as smooth holes that appear in specific internal or surface areas of the castings. These pores are typically only detected after machining. The formation of such cavities is primarily due to gases failing to escape in a timely manner during the investment casting process. To minimize these defects, it is essential to conduct an in-depth summary of the causes and preventive methods of gas porosity in metal casting.
-
1. Possible Causes of Gas Porosity in Precision Metal Casting
- The primary cause of gas porosity in most cases is the insufficient baking of the ceramic shell in precision casting, which allows gases to be trapped and subsequently enter the molten metal.
- Poor permeability of the shell mold, due to shell-making processes or material issues, hinders the escape of gases from the mold cavity, leading to their entrapment in the metal and the formation of pores.
- Air entrapped during the pouring process that fails to escape from the molten steel can result in porosity in the casting.
2. Preventive Methods for Gas Porosity in Precision Metal Casting
-
Set
vent holes at complex structural areas of
the casting where technically feasible in investment casting.
The design of vent holes in investment casting plays a crucial role in casting quality and process stability. Properly placed vent holes effectively expel gases, preventing casting defects. They provide an escape path for air inside the mold cavity, gases evolved from the molten metal, and volatiles released from coatings and sand cores upon heating. This prevents gases from being entrapped in the metal during mold filling, thereby reducing defects like gas porosity, pinholes, and shrinkage porosity. Simultaneously, they reduce gas pressure inside the cavity, improve the mold-filling capability of the molten metal, and prevent issues such as casting deformation or misruns caused by high pressure. -
Fully
consider the shell mold's exhaust requirements when
designing the gating system.
In investment casting mold design, thoroughly considering and implementing an exhaust system offers multiple technical benefits. The exhaust system promptly removes air from the mold cavity, gases generated by sand cores, and hydrogen evolved from the molten metal, preventing gas entrapment during filling and reducing defects like gas porosity and pinholes. For instance, the smooth escape of hydrogen lowers its solubility in the metal, helping to avoid micro-cracks in the casting. -
Ensure
reasonable shell baking temperature, duration, and sufficient holding
time.
This ensures adequate removal of volatiles, optimizes shell properties, and safeguards casting quality. An appropriate baking regime improves the shell's permeability and high-temperature strength, ensuring smooth mold filling by the molten metal and reducing the risk of shell leakage. Sufficient holding time allows for uniform heating throughout the shell, minimizing temperature differences during pouring. This enhances molten metal fluidity, reduces defects like misruns and gas porosity, and is particularly critical for high-precision castings in fields such as aerospace. -
Appropriately
reduce the distance between the ladle spout and the pouring cup, maintain
a uniform pouring speed, minimize air entrainment into the molten steel,
and allow gases in the cavity and molten steel to escape smoothly.
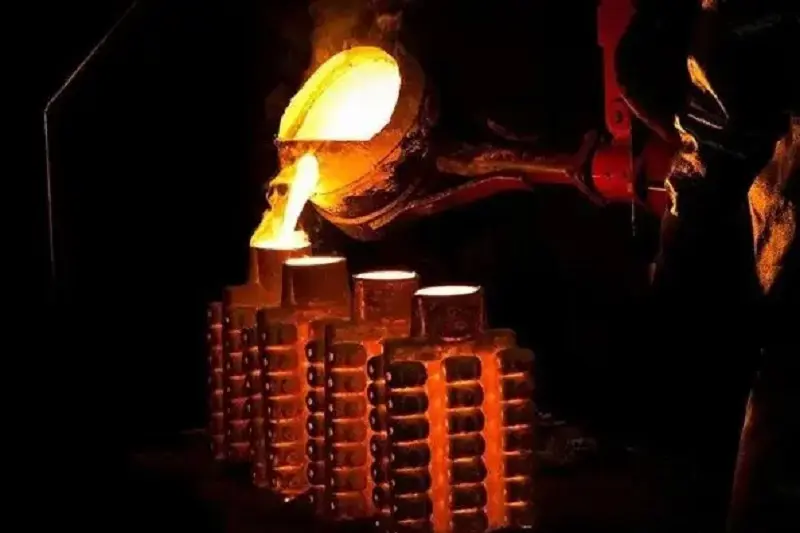
To prevent gas ingress, furnace charge materials must be dry and ensured to be free from moisture, oil contamination, or rust before use. Furthermore, tools that contact the molten metal, such as slagging rods, sample spoons, and ladles, must be adequately pre-heated (baked) before use to eliminate any moisture or contaminants. -
Ensure
complete wax removal during the dewaxing process.
Thorough wax removal during dewaxing effectively reduces residue within the mold cavity, thereby decreasing defects like gas porosity and inclusions. This enhances casting density and improves surface finish.
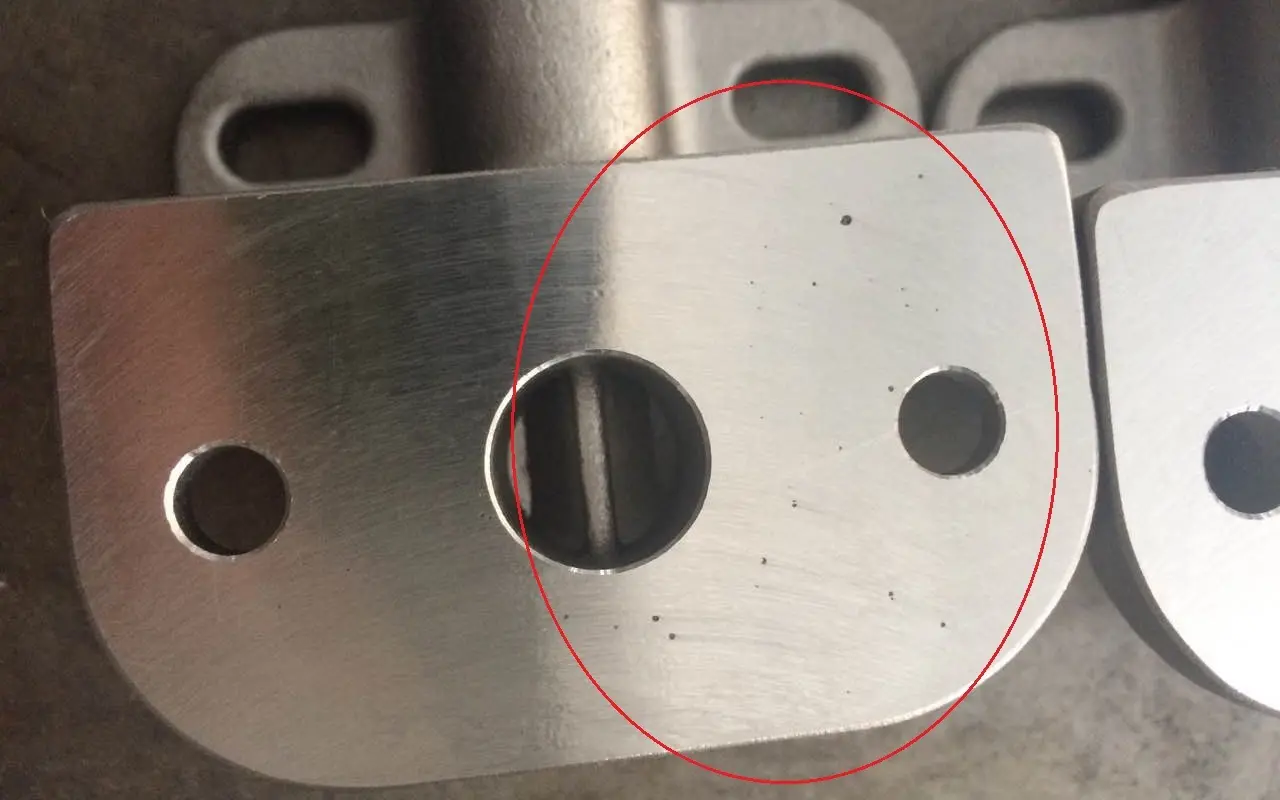

Preventing gas porosity in investment castings fundamentally relies on establishing a stable and well-controlled process system. Beyond the points mentioned earlier, it is essential to strictly regulate the quality of shell baking and the purity of the molten metal to minimize gas sources at the origin. Additionally, precise control over pouring temperature, speed, and shell preheating temperature is necessary to avoid gas entrapment or generation due to process fluctuations. Comprehensive management of production environment humidity and raw material batch consistency is also required. On this foundation, optimizing the design of the gating and riser systems, along with utilizing advanced analytical technologies to ensure smooth mold filling and establish effective venting pathways, is crucial. Ultimately, through standardized operations and continuous monitoring of key process parameters, systematic prevention of gas porosity—from source to finished product—can be achieved.