+86 180 0293 5268
+86 180 0293 5268
What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
In today's manufacturing industry, CNC machining technology plays a pivotal role and is indispensable across almost all sectors. Among its various processes, CNC milling and CNC turning are two of the most common and core machining methods. Both utilize programmed control of machine tool movements to produce parts with high precision and efficiency. However, they differ significantly in their machining principles, applications, and the types of parts they can produce. Below, we explore their differences.
-
- 1. Fundamental Difference in Machining Principle: Motion Mechanism
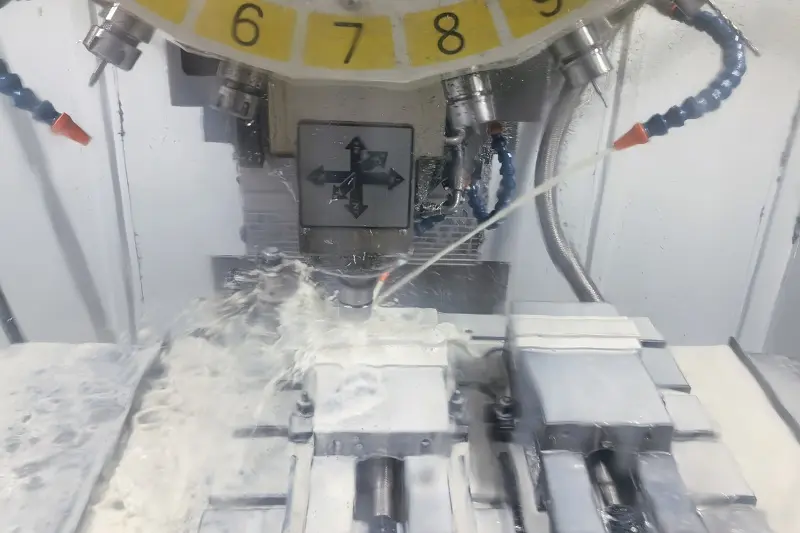
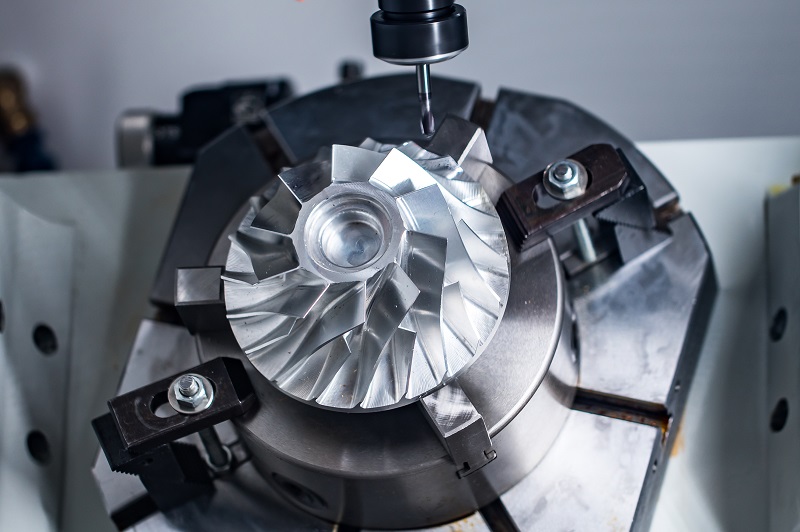
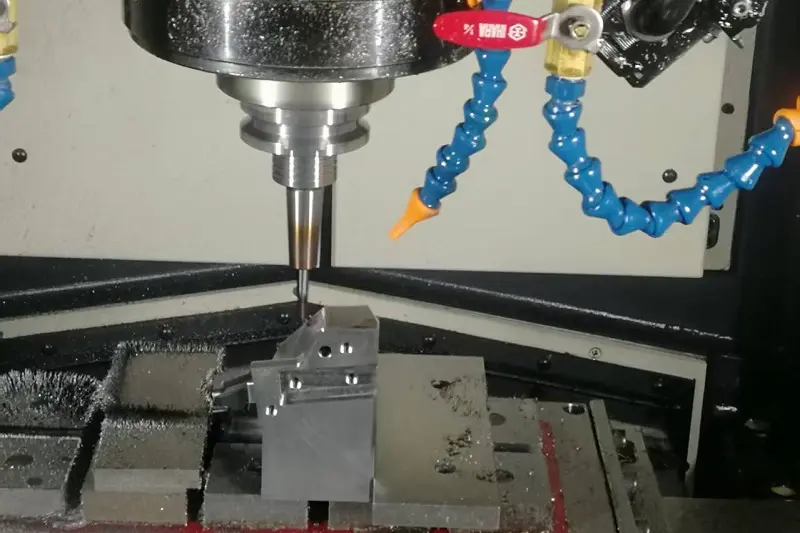
CNC Milling: During milling, the workpiece undergoes linear motion without high-speed rotation, while the milling cutter rotates at high speed to remove material. Milling cutters typically feature multiple cutting edges, enabling machining from various angles. This makes milling ideal for producing parts with complex shapes, such as flat surfaces, contours, grooves, and irregular profiles.
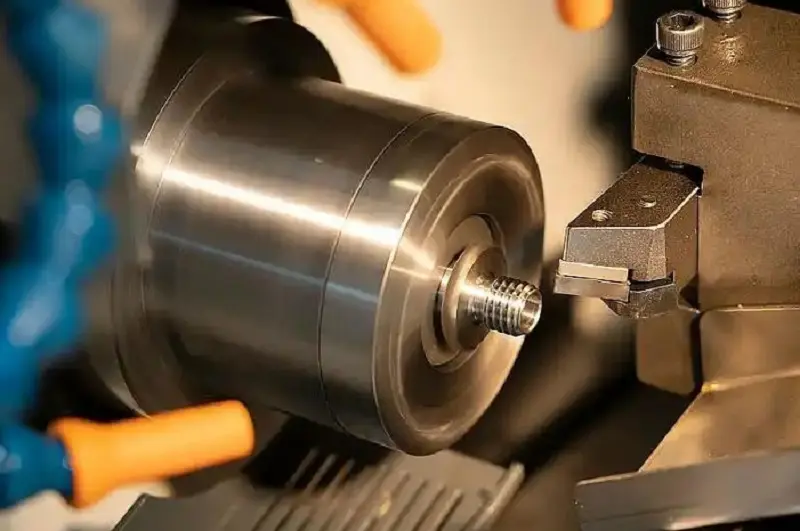
CNC Turning: In contrast, during turning, the workpiece is clamped and rotates at high speed, while the cutting tool remains stationary or moves along a specific path. Material is removed as the tool contacts the rotating workpiece. This method is primarily used for machining rotational parts, such as cylinders, cones, threads, and spheres.
-
2. Tool-Workpiece
Motion Relationship
To better visualize the interaction between the tool and the workpiece, consider the following analogy:
Milling can be likened to a sculptor using a chisel (milling cutter) to meticulously carve a piece of wood (workpiece). The wood remains fixed or moves linearly, along curves, or in specific patterns. The sculptor can create intricate designs and shapes, relying on the sharp chisel (high-speed rotating milling cutter) to remove material.
Turning, on the other hand, resembles a potter shaping clay on a spinning wheel (workpiece). By simply placing their fingers (cutting tool) on the rotating clay, they can effortlessly form a perfect bowl or bottle.
- 3. Applications and Advantages
-
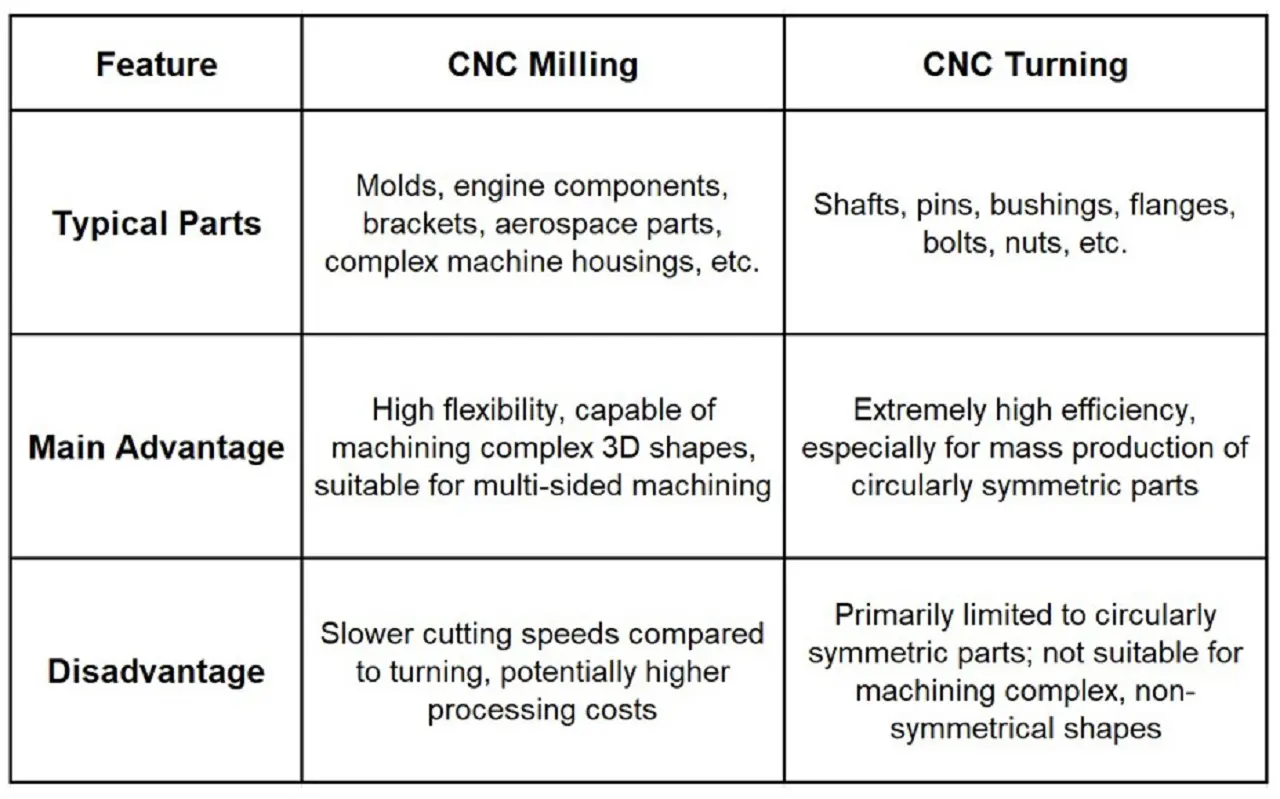
- In summary, CNC milling and CNC turning are complementary technologies in the CNC machining industry.
- CNC milling is renowned for its unparalleled flexibility and ability to handle complex geometries, making it the preferred choice for manufacturing high-value, asymmetrical parts.
- CNC turning stands out for its exceptional efficiency and specialization in producing circular parts.

Looking ahead, with advancements in smart manufacturing and automation, CNC machining technology will continue to evolve, delivering higher-quality, more precise, and increasingly innovative products.