+86 180 0293 5268
+86 180 0293 5268
Which types of parts are suitable for CNC turning?
CNC turning is one of the indispensable and critical CNC machining methods in modern manufacturing. It enables automated processing through numerical control technology, allowing for the efficient and precise machining of a wide range of complex parts. Compared with conventional turning machining, CNC turning offers higher production efficiency and greater machining accuracy, making it suitable for processing various types of components.
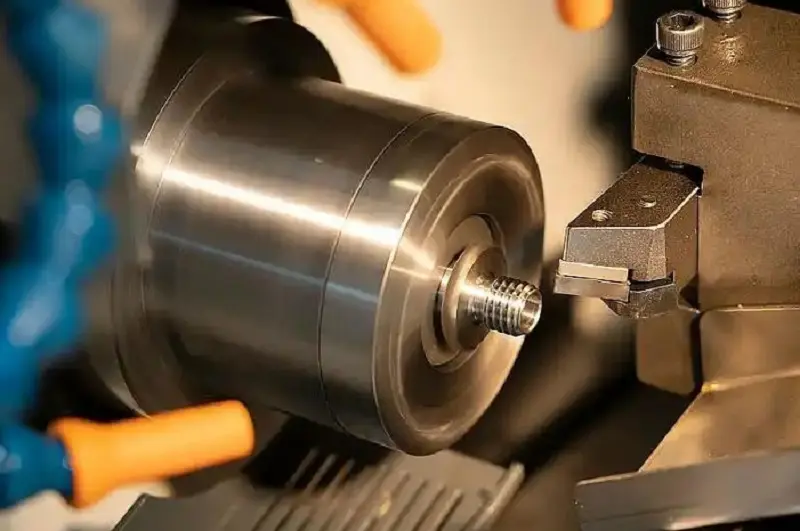
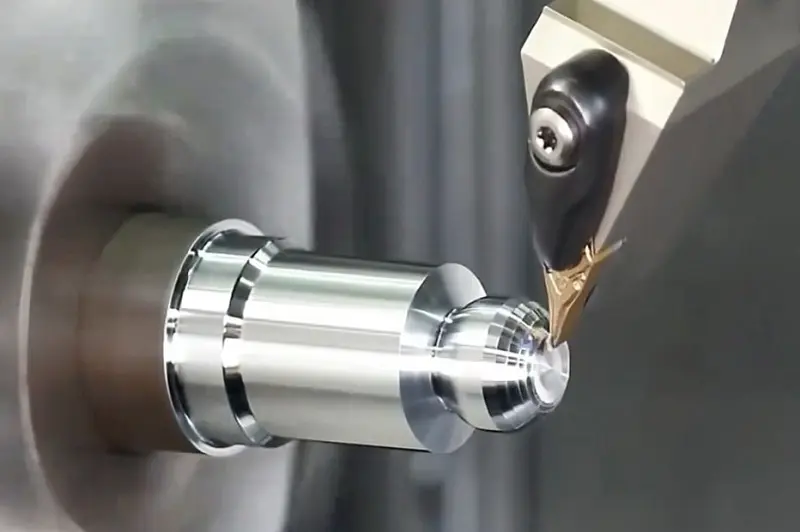
CNC turning is carried out using a CNC lathe. So, what is the working principle of a CNC lathe? A CNC lathe is a machine driven by a computer control system. By precisely controlling various parameters (such as spindle speed, feed rate, tool position, etc.), it achieves efficient and high-precision part machining. CNC lathes are typically equipped with automatic tool changers, which can swap tools automatically based on processing requirements, significantly enhancing production efficiency.
Thanks to its exceptional machining accuracy and flexibility, CNC turning is well-suited for producing a diverse array of parts. Next, let’s explore what types of components are particularly suitable for CNC turning.
-
-
1. Circular Parts
One of the most common applications of CNC turning is machining circular parts. These include various shafts, gears, threads, etc., typically featuring symmetrical external geometries. CNC lathes can efficiently perform operations such as turning and milling, ensuring high precision and superior surface quality. For components with stringent accuracy requirements—such as precision shafts and bearing housings—CNC turning is an ideal processing choice.2. Threaded Parts
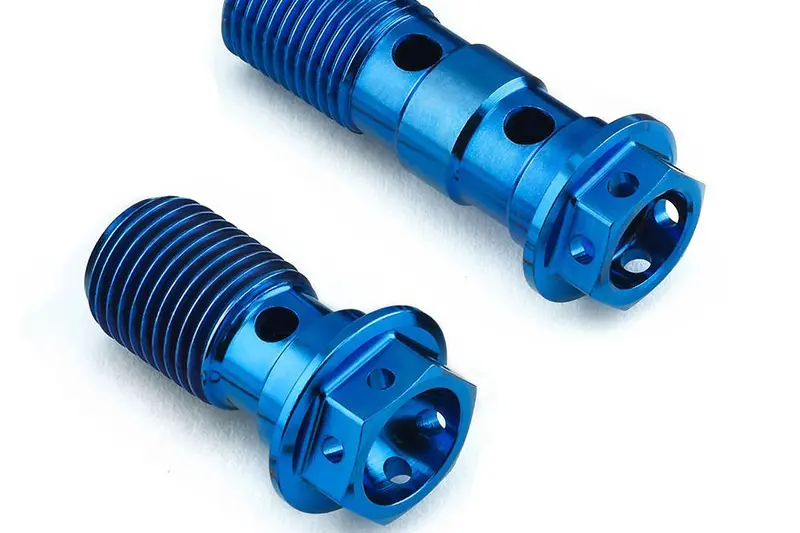
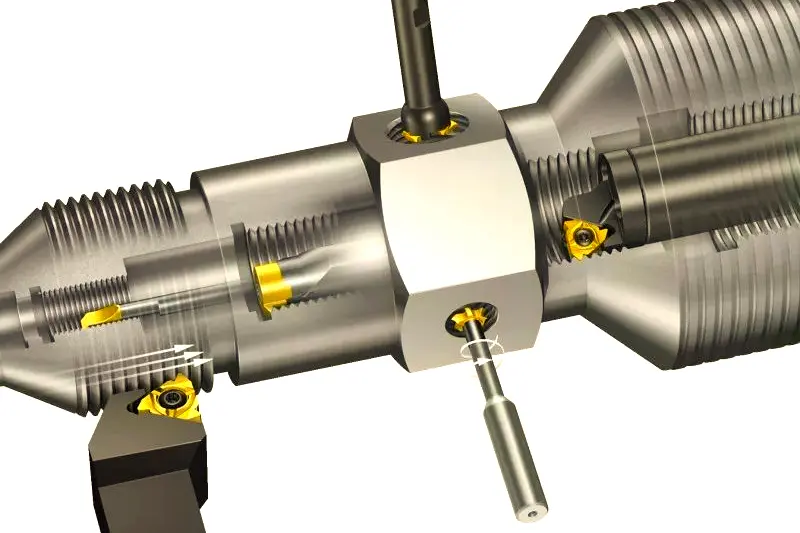
Threaded parts generally require high machining accuracy and surface quality. CNC turning can precisely cut various external and internal threads through its dedicated control system. Whether single-start or multi-start threads, CNC turning automatically adjusts cutting conditions according to set parameters to produce qualified threaded components. This is widely applied in manufacturing bolts, nuts, and similar parts for industries such as automotive and aerospace.3. Non‑Circular Parts
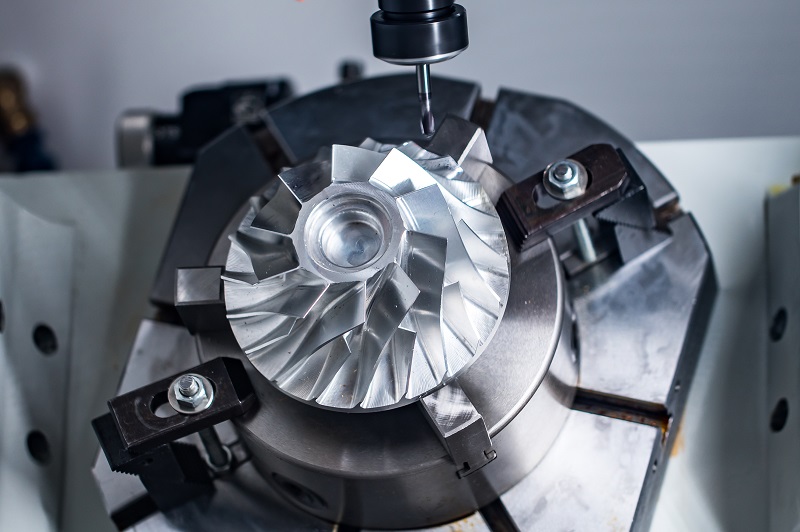
Beyond circular parts, CNC lathes can also machine certain non‑circular components. Through multi‑axis interpolation and sophisticated programming, CNC lathes can produce a variety of non‑circular shapes such as ellipses, squares, and specially contoured holes. Such parts are commonly used in precision machinery, medical devices, and other fields where extremely high accuracy and dimensional stability are required.4. High‑Volume Part Production
CNC turning also offers significant advantages for mass‑produced parts. By automating the production process, CNC lathes minimize human‑induced errors and ensure consistent and stable output. Especially when parts have simple geometries and uniform machining requirements, CNC lathes can complete large‑batch production in a short time, greatly improving efficiency. Typical high‑volume parts include automotive components and household appliance parts.5. Multi‑Functional Part Machining
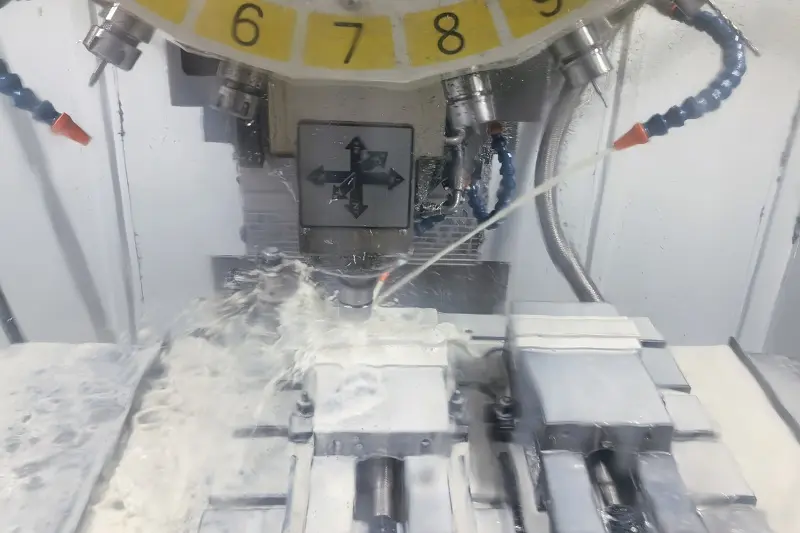
Modern CNC lathes not only perform traditional turning operations but also integrate milling, drilling, tapping, and other multi‑process capabilities. This enables CNC lathes to handle parts with complex structures and varied functions. For instance, certain intricate mold components may require turning, milling, drilling, and other operations. CNC lathes offer exceptional flexibility in such scenarios, efficiently completing multi‑step machining tasks.6. Parts Made of Complex Materials
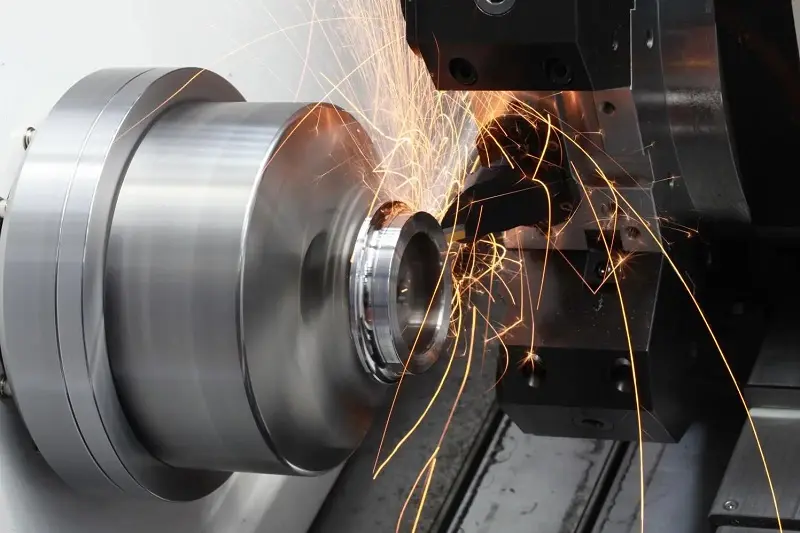
CNC turning is suitable not only for traditional metals but also for high‑strength, wear‑resistant, and corrosion‑resistant special materials such as cemented carbide, stainless steel, and titanium alloys. For these hard‑to‑machine materials, the high‑precision control system of a CNC lathe effectively reduces tool wear, maintains excellent machining results, extends tool life, and lowers production costs.
-
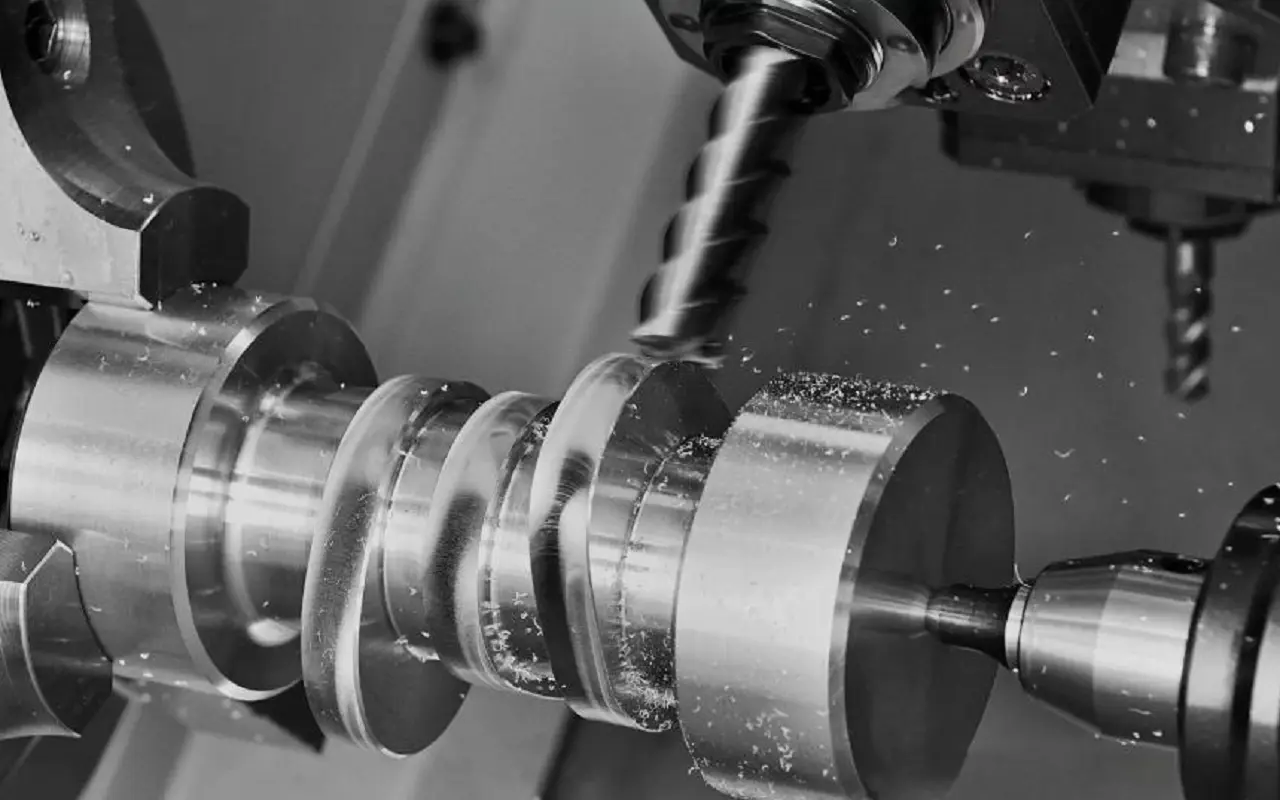

CNC lathes, thanks to their outstanding performance, offer numerous advantages in the field of precision CNC machining. First, they can efficiently and accurately process various complex parts, enhancing production efficiency while ensuring component quality. CNC lathes are capable of machining parts across a wide dimensional range—from tiny components to large-scale workpieces. They can handle cylindrical parts with diameters ranging from a few millimeters to several meters, as well as rod-shaped parts with lengths from millimeters to meters, and can also process a variety of non-circular shapes. Additionally, CNC lathes support high-speed and micro-scale machining, enabling the production of high-precision and miniaturized components.
Second, CNC lathes exhibit strong adaptability, allowing flexible adjustments to meet diverse part requirements. They are suitable not only for single-part production but also for high-volume manufacturing. CNC lathes can process a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics, and can produce parts in various shapes—such as holes, cams, and gears—as well as components of different sizes, from miniature to large-scale. Furthermore, CNC lathes significantly reduce manual intervention during operation, minimizing human error and operational risks, thereby enhancing machining stability and consistency.
CNC turning is a highly capable and widely applicable machining method suitable for processing many types of parts, and it exhibits clear complementarity with CNC milling. Whether dealing with circular parts, threaded parts, precision components, non-circular shapes, or mass-produced items, CNC lathes can provide efficient and precise machining solutions. As manufacturing technology continues to evolve, the application fields of CNC lathes will expand even further, solidifying their role as indispensable equipment in modern manufacturing.